Science News
& Faculty Articles
Time Dilation Experiment with Atomic Clock Opens Possibility to Measure Relativistic Effects in Matter in Quantum State

By: William Brown, Biophysicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
The way we measure time is via frequency. To measure spatial dimension, we use a ruler. In classical mechanics we assumed that these measurement devices were static and would measure the same time and length no matter how an observer was moving or where they were located. However, in the late 19th century it was discovered that this “common sense” perspective of the world is erroneous, and a new mechanics was necessitated. Hendrik Lorentz and Henri Poincare described how rulers contract and clocks measuring frequency have a dilation in the rate of "ticks" they read depending on the movement of a given frame of reference— which was described in relation to the aether in Electromagnetic phenomena in a system moving with any velocity smaller than that of light [1] by Lorentz and The New Mechanics [2] by Poincare. These contractions are known as Lorentz transformations and were generalized by Einstein...
The Vacuum Catastrophe

By Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist, Research Scientist at Resonance Science Foundation
One of the largest discrepancies found in modern physics is the ~122 orders of magnitude difference (i.e., 122 zeros!) between the vacuum energy density estimated by observations at the cosmological scale (a density which is represented by the cosmological constant) and the quantum vacuum energy density at the Planck scale as calculated or predicted by quantum physics.
Just to grasp the magnitude of this difference of 122 zeros we must recall that each position in a number refers to an order of magnitude. For instance, 10 is one order of magnitude bigger than 1, and 100 is two orders of magnitude bigger than 1. As we keep adding zeros, we see an increase called exponential. From this perspective, the size of a proton is of the order of 10-15 m (this means that compared to a ruler the length of a meter, the proton is 15 orders of magnitude smaller, or a quadrillion times smaller) and the...
Superconductivity at Room Temperature … and Extremely High Pressure

Adam Fenster for Sciencenews. “When squeezed to high pressure between two diamonds (shown), a material made of carbon, sulfur and hydrogen can transmit electricity without resistance at room temperature”.
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
Superconductivity is the capacity that some materials show to conduct electricity without any resistance. Hence, with no energy loss. Such behavior would provide a huge advantage, since it optimizes the efficiency of all our electronics components and electrical transmission. Applications are endless; improved current technologies, going from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to magnetically levitated transportation and quantum computers.
First observed in 1911, superconductivity required temperatures reaching absolute zero, the point where there is an abrupt transition in the behavior of electrons, that suddenly couple in pairs (called Cooper Pairs), instead of repelling each other, and flow...
Study Reveals Indications of Environmental Sensing by Genetic Apparatus Driving Non-Random Mutation for Directional Adaptation

By: William Brown, Biophysicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
In our study The Unified Spacememory Network: from cosmogenesis to consciousness, we described how quantum information processing pathways in the molecular genetic system of the biological organism order permutations in a non-random fashion that result in natural directional adaptation and evolution. Information exchanges involving quantum mechanisms at the molecular level of the biological system with the environment and the entanglement nexus of the Spacememory morphogenic field give a kind of natural intelligence to the evolvability of organisms, allowing for meaningful adaptations to occur at an accelerated rate beyond what would be possible under purely random genetic mutations. As the evolutionary biologist Andreas Wagner states, “natural selection can preserve innovations, but it cannot create them… nature’s many innovations, some uncannily perfect, call for natural principles that...
Third Planet Detected in Alpha Centauri System, Earth’s Closest Stellar Neighbor

By: William Brown, Biophysicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
“The discovery shows that our closest stellar neighbor seems to be packed with interesting new worlds, within reach of further study and future exploration,” João Faria, lead researcher and astronomer at the Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço, Portugal.
A third planet has been detected orbiting our closest stellar neighbor Proxima Centauri in the Alpha Centauri solar system [1]. The Alpha Centauri system, at only 4.3 light years from Earth, is turning out to be a rich and diverse solar system: with an Earth-like planet named Proxima b that orbits in the habitable zone around the low-mass M dwarf star Proxima B— which we discussed in the RSF article ‘Potential Habitability of Exoplanets’ [2]— candidate planet Proxima c which has a much larger orbit outside of the habitable zone, and now Proxima d, with a mass about a quarter of that of...
Eridanus Supervoid May Explain Cosmic Microwave Background Anomalous Cold Spot

By: William Brown, Biophysicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
A lot of information about the large-scale nature of the universe can be derived from detailed analysis of its ubiquitous thermal electromagnetic field, called the cosmic microwave background (CMB), for instance analysis of suppressed fluctuations at large wavelengths reveals a closed geometry of the universe— a torus-type geometry as we described in the RSF article A New Signature of a Multiply Connected Universe [1].
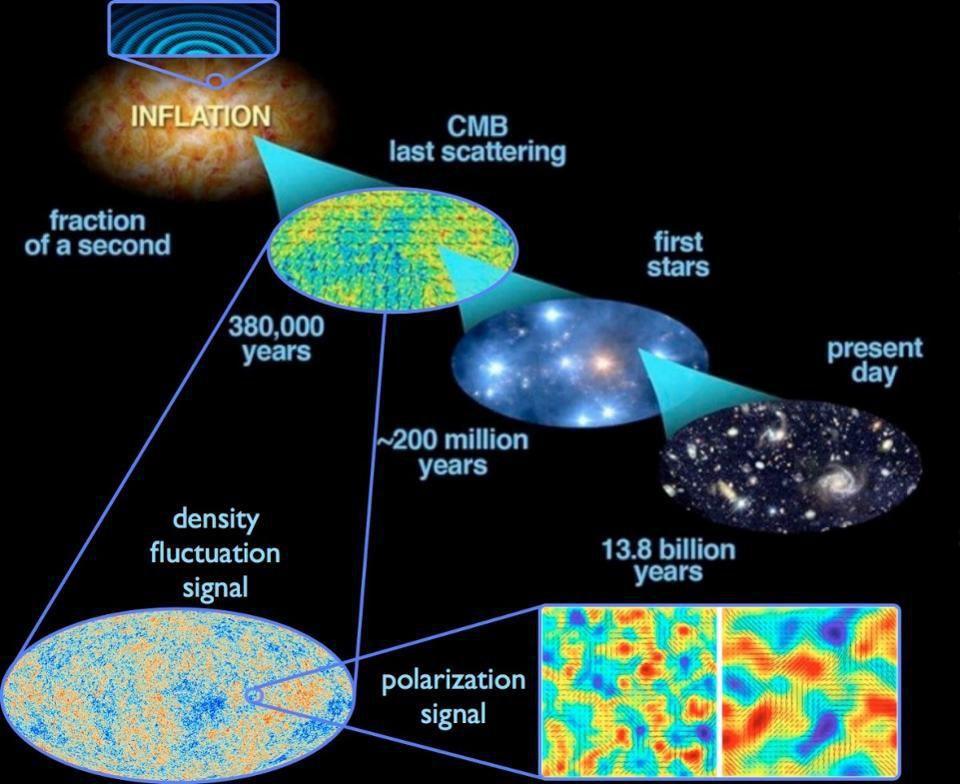
Inhomogeneities attributed to quantum fluctuations during the inflationary period are amplified across large-scale universal structure, and when inflation ends, they become density fluctuations and cause the differences in temperature observed in the CMB. Its an intriguing signal to study because it reveals an epoch when atomistic and cosmological structure where one-and-the same, and quantum behaviors that typify nature evolves into large-scale structural features of the universe. (Credit...
Measuring the Curvature of Space-time Using Time Dilation at Atomic Scale

By physicist Dr. Inés Urdaneta and biophysicist William Brown, research scientists at Resonance Science Foundation
Although quantum mechanics— the physics governing the atomic scale— and general relativity— the physics governing the cosmological scale— are still viewed as disparate regimes within the Standard Model (Haramein's holographic quantum gravitational solution has not reached wide-spread mainstream appeal as of yet), experiments on the quantum scale are reaching the capability of measuring relativistic effects, therefore connecting in practice, what remains disconnected in theory.
Such is the case of the recently observed gravitational Aharonov-Bohm effect—a quantum probe for gravity. In the electromagnetic version of the Aharonov-Bohm effect (in which the highly nonlocal quantum effect was first predicted) an electrically charged particle is affected by an electromagnetic potential, despite being confined to a region in which both the...
Halogen Atom Sigma Hole Viewed for the First Time
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
By functionalizing with a single xenon atom the tip probe of a Kelvin force microscope, a group of researchers from the CATRIN of Palacký University in Olomouc, the Institute of Physics of the CAS, the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the CAS, and the IT4Inovations Supercomputing Center at Technical University of Ostrava have achieved an extraordinary increase in the resolution of atomic scanning microscopy, increasing the sensitivity of the microscopy up to sub-atomic level.
Thanks to this achievement, this group -lead by Pavel Jelínek- was able to capture the real image of the anisotropic (asymmetric) electronic charge distribution -called sigma-hole- on single atoms of halogen compounds. The sigma hole (abbreviated as σ-hole) asymmetric electron density distribution was predicted 30 years ago but never observed before, until now.
This prediction is based on the...
Results of Experiment Reveals that our Understanding of Electrochemistry is Incomplete

By: William Brown, Biophysicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
Textbooks on electrochemistry are due for an update with the results of a recent study of fuel cells measuring the ion activity around an electrode in a salt solution [1]. There is a classical 100-year-old theory that describes what is thought to be the distribution of ions around such an electrode, at the interface with the electrolyte, where the charge of the electrode attracts ions from the solution and forms what is called an electrical double layer—ions of opposite charge from the electrode crowd around its surface, forming a structure of charges at the interfacial layer.

Gaining a more complete understanding of electrochemistry will be salient to important forms of energy storage and production, like those utilizing fuel cells.
Understanding the molecular structure of the electrode–electrolyte interface is essential in elucidating many interfacial electrochemical phenomena such as corrosion,...
Evidence of Black Holes Forming Galaxies is Mounting!

Image from ESA, the European Space Agency.
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
In just one week, two very important studies have shed light on the now irrevocable fact that black holes in the center of galaxies are playing a predominant role in the galaxy formation, event that would explain why astronomers and astrophysicists have found a black hole in the center of galaxies.
In a former RSF article entitled “Supermassive Black Holes Birthing Stars at Furious Rate’ we had addressed the case in which astronomers have observed supermassive black holes creating star-forming regions. Since 2017 a team of astrophysicists have been observing supermassive black holes, and the possibility that these entities could be birthing stars, finding evidence of new star birth from material being ejected from the black hole, called an outflow. An outflow of gas could be responsible for creating new stars by swirling around the center of the black...



