Science News
& Faculty Articles
On the Mystery of Jupiter’s Cyclones Geometrical Patterns and Stability

Cyclones in North pole of Jupiter, by Juno Spacecraft. Image from original paper [1].
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in our Solar System, is a gas giant primarily composed of hydrogen, though helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It is thought to have a rocky core of heavier elements, though it lacks a well-defined solid surface, like the other giant planets in the Solar System. Its outer atmosphere is defined by a series of latitudinal bands, with turbulence and storms along their interacting boundaries. Jupiter is mostly known for its Great Red Spot, a giant storm which has been observed since at least 1831.
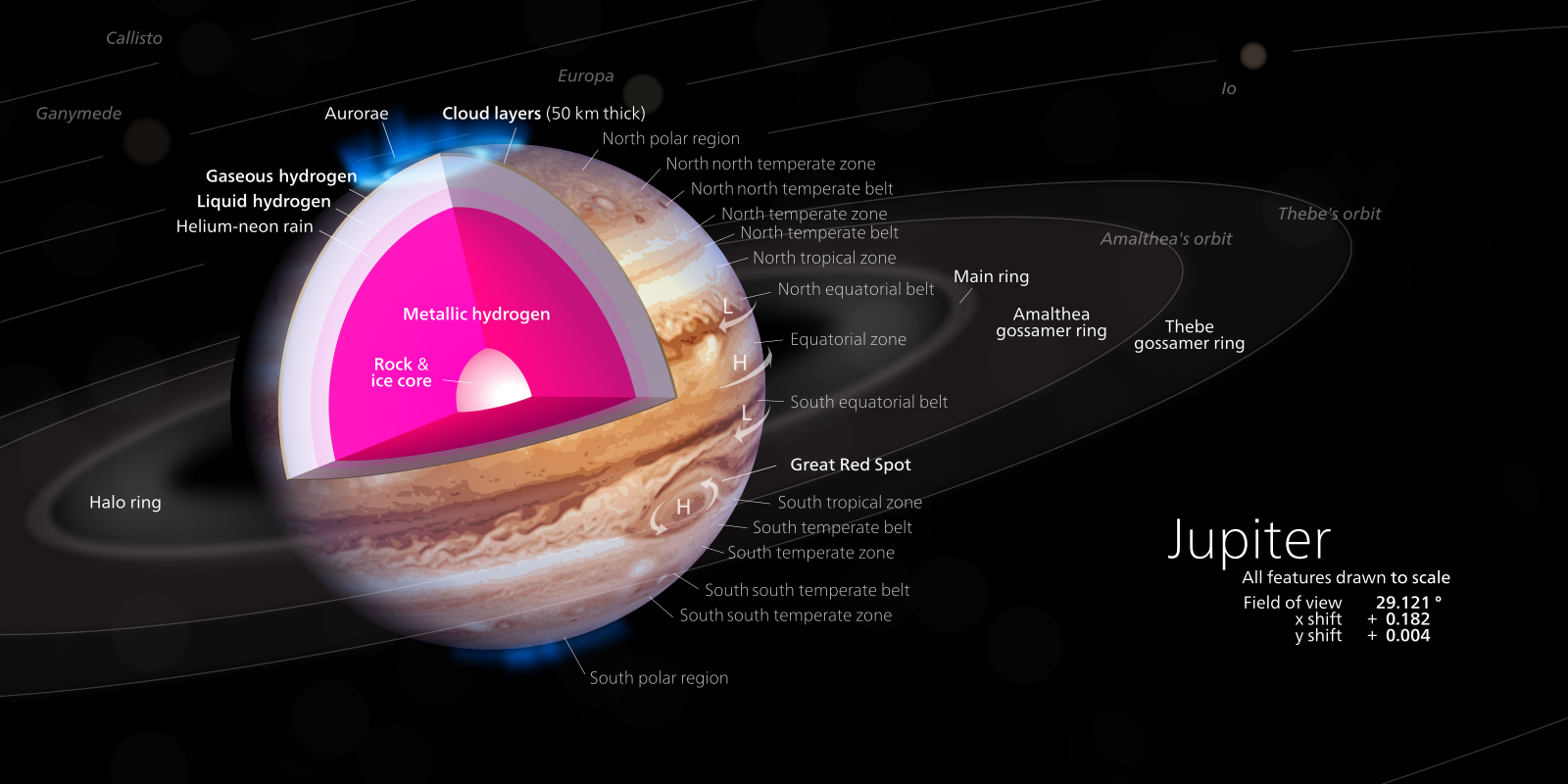 Diagram of Jupiter, its interior, surface features, rings, and inner moons. If Jupiter has an actual core or if there's actually metallic hydrogen inside, is currently purely theoretical. Credit image: Kelvinsong
Diagram of Jupiter, its interior, surface features, rings, and inner moons. If Jupiter has an actual core or if there's actually metallic hydrogen inside, is currently purely theoretical. Credit image: Kelvinsong
Juno spacecraft is the latest probe...
Quark-Gluon Plasma and the Size of the Nucleons

By Amal Pushp, Affiliate Physicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
The atomic nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons bound together via strong nuclear interaction. Due to this, protons and neutrons are also called nucleons. Furthermore, protons and neutrons have inner substructure and consist of a combination of up and down quarks as well as gluons, which are particles mediating the strong force. Physicists usually probe the structure of nucleons with particle collisions in accelerators. Specifically, the development of the quark model in particle physics emerged by investigating the deep inelastic scattering of electrons on protons and bound neutrons for which the investigators were also awarded a Nobel prize back in 1990.
What happens when we heat atomic nuclei at high temperatures? We eventually achieve a new state of matter called quark-gluon plasma. Quark-gluon plasma may be defined as a state of matter in which the elementary...
JWST Image of Rings Around Star WR140 Leaves Astrophysicists Baffled!

With its mid-infrared instrument (MIRI), the James Webb Space Telescope captured the star WR140 surrounded by strange concentric shells that gradually fade away.. (Image credit: NASA/ESA /CSA /Ryan Lau /JWST ERS Team /Judy Schmidt)
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
An image taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in July 2022 showing a star named Wolf-Rayet 140 (WR 140) surrounded by regular ripple-like circles that gradually fade away, was released on Twitter by scientist Judy Schmidt. Star WR140 is in the Cygnus constellation and resides around 5,600 light-years from Earth. The image ignited a torrent of comments, making astronomers and astrophysicists scratch their heads over this unexplained observation.
Wolf-Rayet stars are rare, only 600 have been found, and they’re very short-lived, generating powerful winds that push huge amounts of gas and dust into space, while loosing most of their mass in the process. In this...
The Puzzle of Baryon Asymmetry and the Cosmic Origin of Matter

Credit: M. Weiss / Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
By Amal Pushp, Affiliate Physicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
At the very beginning of our universe, a short phase after the big bang, everything is supposed to have existed in the form of a hot soup of particles, presumably containing equal proportions of matter and anti-matter. As the universe expanded in size, the overall temperature lowered and particles coalesced together to form the various structures that we detect with our modern-day astronomical instruments and technology.
Anti-matter, which is basically the opposite of matter, in most respects behaves just like its matter counterpart, the only key difference is in the charge that it carries. For example, the anti-particle of the electron, a negatively charged particle, is called the positron, which as the name suggests is positively charged. An interaction between electron and positron causes annihilation leaving just photonic radiation behind....
Another Validation of Haramein’s Theory: Physicists Confirm that Black Holes Admit Vortex Structure!

By Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
Understanding the microscopic structure of black holes has been a challenge for physicists. The recent work from Gia Dvali, Florian Kühnel and Michael Zantedeschi entitled Vortexes in Black Holes, and published in Physics Review Letters, is providing a framework from which such understanding can be attained, while at the same time validating Nassim Haramein’s holographic approach.
Dvali et al. propose that black holes could be understood as a graviton condensate at the critical point of a quantum phase transition, based both on a graviton-condensate description of a black hole and on a correspondence between black holes and generic objects with maximal entropy compatible with unitarity; the so-called saturons. Saturons are a saturated state collective behavior of gravitons, i.e., a Bose Einstein Condensate (BEC) of gravitons, situation that is possible when gravitons are confined in a volume of space,...
Scattering Amplitudes Help Physicists Investigate the Behaviour of Sound Waves through Solids

Credit: Grant Remmen
By Amal Pushp, Affiliate Physicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
Scattering amplitudes are a quantum field theoretic concept that allows the computation and representation of various scattering processes involved in particle physics. It is basically a probability amplitude, an entirely mathematical concept, that aids the description of elementary particles and their associated physical systems. This highly rigorous technique is being utilized as a research tool in various subfields of theoretical physics like Yang-Mills theory, Chern-Simons theory, Supergravity (SUGRA), etc.
Conventionally, such computations have been probed using Feynman diagrams, however, it has a limited range of applicability and that’s where scattering amplitudes come in and express their overarching role. For instance, to describe the interactions of fundamental particles, one would have to manually fit thousands of Feynman diagrams into the computer which would make the...
An Eventful Horizon

Scientists utilize elements of the Haramein Quantum Gravity Holographic Solution to solve the Black Hole Information Loss Paradox
By: William Brown, scientist at the Resonance Science Foundation
In our quotidian experience the feature of spacetime locality seems to be an indelible feature of a rational reality; the idea that effects follow their causes gives us a sense (however illusionary) that there is a natural chronology to our reality. From the theory of relativity, we know that the simultaneity of relativity requires that no signal or information travel faster than the speed of light. Faster-than-light, or superluminal signals results in closed timelike curves, and in general relativity closed timelike curves can break causality with remarkable and unsettling consequences. At the classical level, they induce causal paradoxes disturbing enough to motivate conjectures that explicitly prevent their existence (Hawking's chronology protection conjecture). If a signal were to...
The Generalized Holographic Model, Part II: Quantum Gravity and the Holographic Mass Solution

Image credit: Shutterstock
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
In the former article entitled The Generalized Holographic Model, Part I: The Holographic Principle, we introduced the holographic principle as developed by David Bohm, Gerard 't Hooft, Jacob Bekenstein and Stephen Hawking. This principle states that the information contained in the volume of a Black hole is holographically present in the boundary or event horizon of the black hole. We then introduced the generalization of such principle by Nassim Haramein, where he includes the volume information or degrees of freedom in the volume as well. This generalization allows to define a holographic ratio that accounts for the surface-to-volume entropy or information potential transfer, which is a steady state or thermodynamical equilibrium, equivalent to a kinetic rate constant.
In this second part we will see why Haramein’s generalized holographic approach gives a quantized...
Probing Quantum Magnetism with Near Absolute Zero SU(N) Atoms

By Amal Pushp, Affiliate Physicist at the Resonance Science Foundation
Absolute zero is the temperature at which all physical dynamics come to a halt. The laws of physics however do not allow us to attain absolute zero. This fact unfolds from a fundamental feature of quantum mechanics according to which fluctuations are always occurring at the quantum level and the quantum particles always have enough energy to continue their dynamical motion unlike in a classical system. Such a system contains quantum mechanical energy even at absolute zero and this energy is technically called zero-point energy. However, physicists can achieve temperatures close to absolute zero in an advanced laboratory. Examples where working near absolute zero is common include quantum phenomena like Bose-Einstein condensation, superconductivity, superfluidity, etc.
Now in yet another situation, physicists from Japan and the US have succeeded in cooling atoms of Ytterbium (an element also used in making atomic...
The Generalized Holographic Model, Part I: The Holographic Principle

By Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
The holographic principle is one of the first introductions of the idea that information may be present holographically within certain structures in the universe — namely, black holes. At this point, one may start to notice how the scientific narrative has been progressively and very subtly switching from terms like energy, forces, particles, and fields, to this word: information.
When we think of information, we think of computers and programming and bits of information, expressed in values of 0 or 1 in a binary system. This all is a subset of a larger field called information theory, whose goal is to explain all features of reality as emerging from information exchange and its properties.
This article explores further the topic, giving a brief overview of the history and development of the holographic principle behind the fundamental concept of the generalized holographic model developed by Nassim...



