Science News
& Faculty Articles
Is the Universe Expanding at an Accelerated Rate?

by Dr.
A new study challenges the cosmological model and suggests that the universe is not expanding at an accelerated rate.
The standard model of cosmology assumes that the universe is isotropic with no preferred direction and no preferred frame of reference; that is, we are not special and our position in the universe is not from a privileged vantage point. Within this framework, observational data led us to the conclusion that 70% of the universe is expanding at an accelerated rate, and this accelerating force is due to an unknown form of energy known as ‘dark energy’. This so-called ‘dark energy’ is now thought to be due to quantum fluctuations of the vacuum energy.
However, a new study by a team of European scientists explored these ideas further. They wanted to see what would happen when they measure the deceleration parameter – the measurement of cosmic acceleration – from our...
Tuning Cells for Health and Wellness

by
Resonance-based technologies utilize harmonic interactions to effortlessly produce significant effects. This is why the potential for applications in energy production is so promising: methods employing harmonic resonance can do more with less energy. Additionally, technologies employing harmonic resonance offer a potential means for benefiting health and wellness of the biological system without deleterious side-effects.
With such potential applications, Torus Tech is developing the resonant modulation capabilities of its plasma-hydrodynamic and harmonic frequency technologies to direct beneficial signaling in the extra-cellular matrix for restorative and bio-regenerative therapies. Such techniques offer a highly efficacious and non-invasive method to restore healthy operations of the body and to target specific conditions such as injury and cancer.
The extra-cellular matrix (ECM) is a part of the body-wide...
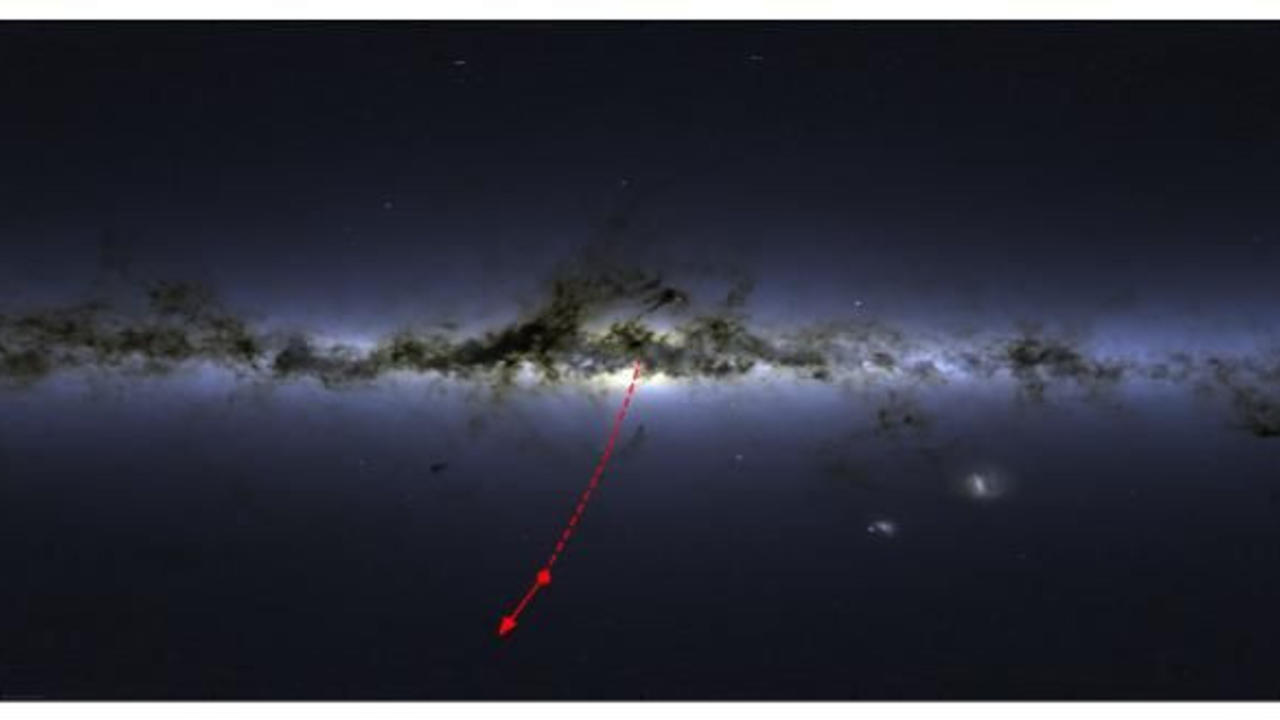
Was a Star Ejected from Our Central Black Hole?

by
Generally thought to be the point of no return, our very own black hole seems to have ejected a star at hyper velocity.
In something known as the Hills mechanism – which occurs in binary star systems when they are disrupted by a super massive black hole – the stars are pulled apart and left to continue on their separate journeys. The closest star is pulled into an orbit around the black hole while the other is ejected at extremely high velocity. However, although this was proposed in 1988 by astronomer Jack Hills, it has never been confirmed.
Now, a worldwide team of scientists led by Ting Li have observed what they believe to be the first example of such a mechanism.
The team utilised data from the 3.9 metre Anglo-Australian Telescope as part of the Southern Stellar Stream Spectroscopic Survey – a survey that aims to map the kinematics and chemistry of long, dense regions of stars, known as...
The Force of the Vacuum

by Dr.
One of the most common physical manifestations of the vacuums’ force is the Casimir effect, which was first predicted by the Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir in 1948, and measured for the first time by Steven Lamoreaux in 1996. Nonetheless, the physical interpretation and whether or not the effect comes from the vacuum fluctuations, is still under discussion in theories of quantum gravity and quantum electrodynamics. It also remains a mystery that the energy density of the vacuum is so high it should act gravitationally to produce a large cosmological constant, as well as curving spacetime. And yet, there is a difference of 122 orders of magnitude between the classical vacuum represented by the cosmological constant, and the quantum vacuum energy density. This discrepancy is known as the Vacuum catastrophe (Investigation of the gravitational property of the quantum vacuum may explain the accelerating...
Could the Information Paradox Finally Be Resolved?

by
The information paradox may finally be resolved with the help of the holographic theory – but this time on a fractal scale.
Ever since Hawking predicted the thermal emission of black holes and their subsequent evaporation, the question arose as to where this information goes. In the context of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics – which states that the information about a system is entirely encoded in its wave function – information is always conserved. Thus, any loss in information, like that predicted by Hawking and his evaporating black holes, would violate quantum theory. This problem is known as the information paradox.
To resolve this paradox, physicists have been actively looking for a mechanism to explain how the information of the infalling particles re-emerges in the outgoing radiation. To begin, they need to determine the entropy of the Hawking radiation.
Assuming the...
Ancient Light Suggests Universe Could Loop Back on Itself!

Image: The cosmic microwave background as seen by the European Space Agency’s Planck satellite. Credit: ESA and the Planck Collaboration
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
The photo above is quite common among astronomers and astrophysicists. It depicts what is known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB), the very ancient light coming from the beginnings of our universe. It is supposed to be the leftovers of the grand explosion birthing our Universe, called the Big Bang.
When analyzing the expansion of the universe, astrophysicists imagined that the expansion could be rewinded, just like a film, and that this backward movement would show the collapse into a singularity. Together with the astronomical observations of the CMB radiation, they concluded that the universe had to be flat. But recent observations with better precision are showing a different picture. An anomaly in data from the best-ever measurement of the CMB is offering...
The Far Reaches of the Cosmic Web

by Dr.
Galaxies seem to be communicating with each other across vast distances never thought possible before, putting the cosmological principle into question again.
These gravitationally bound structures consisting of gas, dust and trillions of stars exist in the trillions. Most observed galaxies are spiral galaxies like our very own Milky Way, with others being elliptical, lenticular or irregular. The formation and evolution of a galaxy is generally revealed in galactic kinematics, particularly the rotation which is constrained by the conservation of angular momentum. Through studying the rotation of galaxies, scientists can thus infer how the galaxy was formed and how it evolved. Did it form from a rotating dust cloud? Did it evolve as a merger?
As would be expected, galactic behaviour – including its rotation – is influenced by that of its neighbours. However, in a recent report, Korean scientists Joon...
Supermassive Black Holes Birthing Stars at “Furious Rate”!

By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
We have been increasingly hearing much more about black holes and their role in the cosmos.
Black holes are exotic creatures, mainly classified in two types according to their size: stellar black holes (up to tenths of solar masses) and supermassive black holes (billions of solar masses). We commonly used to believe that, independent of their size, black holes all share the same feature: they devour everything getting too close and entering their event horizon.
For decades, astronomers have looked for galaxy clusters containing rich nurseries of stars in their central galaxies. Instead, they found powerful, giant black holes bursting out energy through jets of high-energy particles. Extremely hot particles emanating from these black holes were found to be preventing the formation of stars. So where are all the stars coming from?
The leading theories have proposed two mechanism to elucidate this mystery. One...
NASA’s Helical Engine Design that Uses Closed-Cycle Propellant; A Proposed Stardrive that May Enable Interstellar Travel

by
Twentieth Century technology has relied on the use of fuels and chemical propellants to propel our ships, planes, and cars. The propulsion technology of the future will not use chemical combustion to produce thrust, and the 21st century will see the emergence of propellant-less propulsion systems. Such technologies will provide the means to travel faster than ever before at a fraction of current costs and with no pollution by-products.
This becomes absolutely crucial for interplanetary and interstellar travel, as we have stated before in RSF commentary1 reporting on Resonance-based technology may provide inertial mass reduction—the future of space travel will not be performed with chemical propellants. As an example, to date the most viable proposal for an interstellar mission with current technological capabilities is the Breakthrough Starshot project which will use a fleet of light sail probes propelled to...
Protons in Life
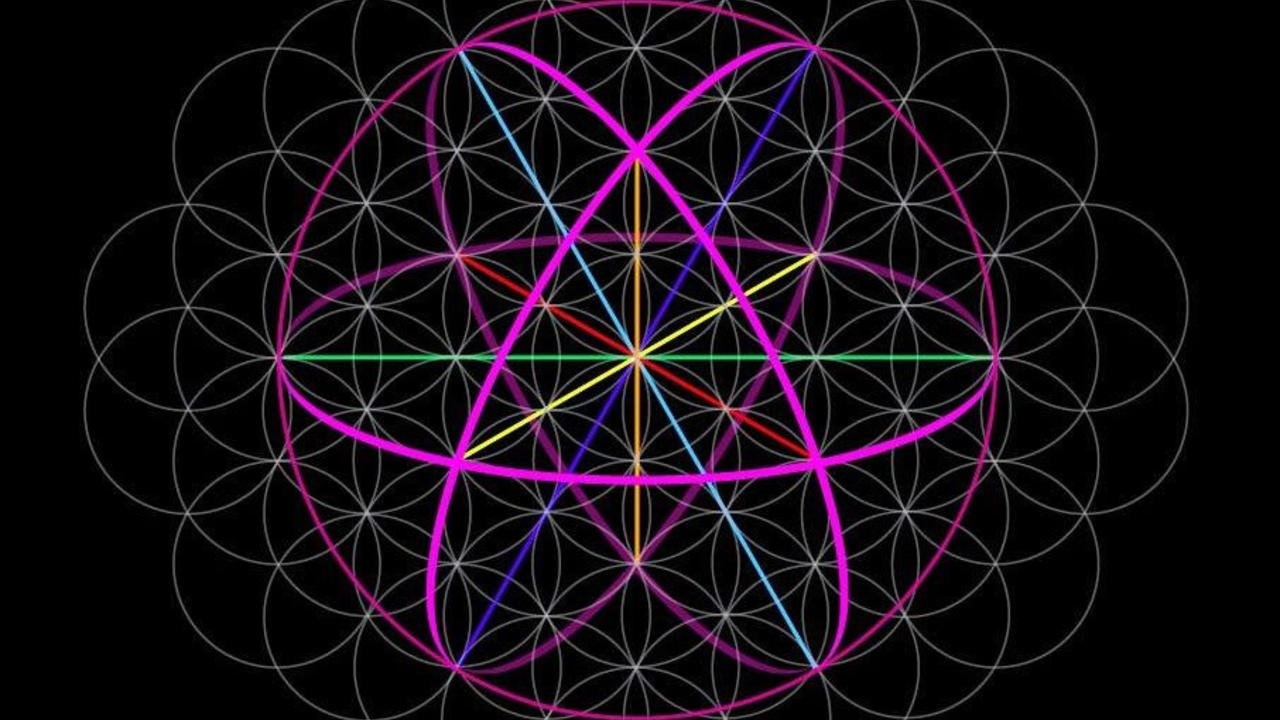
by
Image by Marshall Lefferts http://cosmometry.com/. See RSF in Perspective below for more info on this image.
Just recently, new experimental data on the charge radius of the proton was published in Science, confirming Nassim Haramein’s 2012 prediction based on his Holofractal Universe Theory as being exact. Previously, Nobel Laureate Hideki Yukawa and others gave hints the charge radius could be smaller than the current paradigm standard estimated. For us it is very important that the prediction is a result of a much broader theoretical perspective based on Quantized Gravity, Spin Dynamics and Unified Physics. Now, why could this be important for your everyday life?
Haramein’s Generalized Holographic Approach successfully predicts many more observed parameters (micro- and macrocosmic) and allows biological processes to be integrated as well. Life must no longer happen in undefined physical realms. We...



