Science News
& Faculty Articles
Novel Geometric Model Allows for Better Categorization and Prediction of the Properties of Natural Spiraling Phenomena

By: William Brown, Resonance Science Foundation biophysicist
Robert Grant and his research team Talal Ghannam and Amanda Kennedy have published a study describing a novel class of triangular spirals based on right triangle polygonal modular formations. These new forms are shown to match many natural spiraling phenomena better than any previously proposed model. The improved model will allow for better categorization and prediction of the properties of numerous spiraling formations manifested in the natural world, and hints at a possible fundamental role for right triangular geometry in morphogenesis and the natural laws of the physical universe.
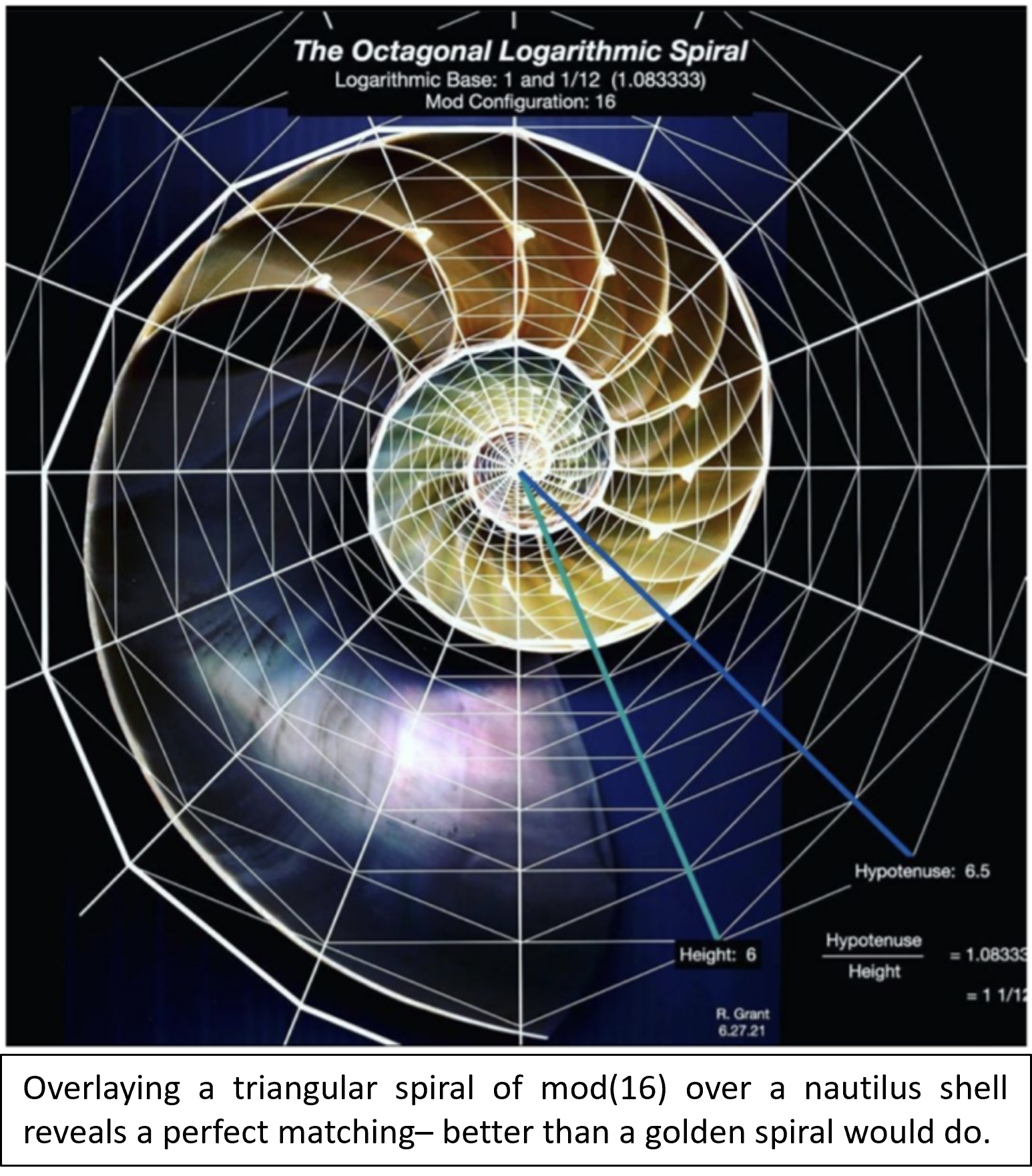
Spiral formations abound in nature, from the micro to the macro, from the spiraling oscillation of electromagnetic waves, to molecules like the information-carrying polymer of DNA, to the body patterning of organisms, tornadoes, hurricanes, planet-sized vortices on...
Quantum Simulator Reveals New State of Matter Possible with Topological Spin Liquids

By Resonance Science Foundation biophysicist William Brown
Quantum spin liquids are exotic phases of matter that offer potential applications in robust quantum information processing with topological qubits. Quantum spin liquids are a phase of matter that feature long-range quantum entanglement involving the magnetic dipoles, or spin, of electrons. Unlike in conventional magnets where the magnetic dipoles of electrons all align and freeze into place, electrons in this new exotic phase are constantly changing and fluctuating like a liquid— leading to one of the most entangled states of matter ever conceived.
Until recent investigations it was unknown if such a highly quantum correlated magnetic state could be realized in an actual physical system. Now, using a 219-atom programmable quantum simulator a team of Harvard researchers have shown that quantum matter and protected quantum information processing are possible with topological spin liquids. Their findings...
Extraterrestrial Technosignature Still a Viable Explanation for 'Oumuamua, was it an Interstellar Probe?

By biophysicist William Brown, research scientist at RSF
In 2019 we reported on the first interstellar visitor to our solar system and the interesting proposal by Harvard astronomer Avi Loeb that it could be a possible technosignature of extraterrestrial engineering. Loeb proposed this hypothesis to answer many of the anomalous observables of the interstellar visitor, named 'Oumuamua, such as its oscillating reflectivity— indicating that its profile is changing from a large area to a smaller one, so that it is either flat like a solar sail, or long and thin like a cigar shape and tumbling— the lack of any outgassing as it passed by the Sun, and its anomalous trajectory whereby it accelerated as it left the gravitational well of the Sun and our solar system.
Loeb further expounds that the sudden acceleration and deviation of 'Oumuamua from its expected orbit appeared to be the result of radiation pressure, which is precisely how solar sails achieve propulsion....
Warp Field Mechanics of the Dynamic Vacuum

By biophysicist William Brown, research scientist at RSF
Crawl-walk-run. This is the motto of Harold "Sonny" White— former director at NASA's Eagleworks division for advanced propulsion physics research— to put into perspective the proper technological progression required for developing a warp drive. True to this grounded perspective on how a remarkable civilization-changing technology can become a reality, Dr. White has published empirical simulation data of a nanometer scale warp bubble— a spacetime geometry that enables novel propulsion via gravitational control— that albeit too small for practical applications of propulsion, is experimental indication that the energy density requirements for a warp drive are technologically feasible.
This is an important demonstration, as a common objection to warp drive technology—and even the use of wormholes—is the seeming requirement for negative energy densities, which many physicists...
Geometrical understanding of entropy!

Image: Ari Weinkle for Quanta Magazine
By physicist Dr. Ines Urdaneta and biophycisist William Brown, research scientists at Resonance Science Foundation
In a former RSF article by biophysicist William Brown and astrophysicist Dr. Amira Val Baker, entitled “The morphogenetic field is real and these scientists show how to use it to understand Nature”, they address the work from Chris Jeynes and Michael Parker, published in Nature 2019, which concludes that there seems to be a field of information-entropy responsible for shaping the micro (DNA strands) up to the cosmological scale (spiral galaxies like the Spira Mirabilis, a double logarithmic spiral). This field of information would give a theoretical support to what biologist Dr. Rupert Sheldrake would call, the morphogenic field!
In the case of the galaxies, Jeynes’ and Parker’s calculations show that the postulation of dark matter (which has not been detected yet) is superfluous, since the entropic...
CODATA Proton Charge Radius; The History Of This Fundamental Measurement

Haramein’s holographic solution accurately predicted the mass and radius of the proton in 2012 [2, 3], resulting in a radius 4% smaller than the Standard Model and experiments gave at the time. This prediction that does not utilize adjusting parameters, was later confirmed at the Paul Scherrer Institute utilizing muons in a proton accelerator. Further experiments utilizing electrons confirmed the radius in 2017-2018. The value of the proton RMS charge radius has since been validated by the adjusted 2018 CODATA value, which is the standard for all fundamental physical constants.
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
It’s been almost two years since the charge radius of the proton was finally confirmed experimentally by a September 2019 study from Eric Hessels [1], of York University in Canada, and his colleagues.
In his paper entitled Quantum gravity and the holographic mass (published in 2013, though the work was sent to...
The Universe Organizes in a Galactic Neuromorphic Network

Article by William Brown, Biophysicist, Resonance Science Foundation Research Scientist
The Universe Organizes in a Galactic Neuromorphic Network
The Quantitative Comparison Between the Neuronal Network and the Cosmic Web

A key observation in the science of a unified physics of reality is that the universe appears to follow a self-organizational patterning utilizing properties of holography and fractals. These two features of organizational structure in the universe are so ubiquitous that us researchers at the Resonance Science Foundation often refer to “holofractogramic physics” to simultaneously describe an organizational system that is both holographic and fractal in nature. This refers to two properties of universal organization that seem to be primary: holographic ordering of information—in which any subunit of a system contains information about the whole— and fractal ordering of structure.
What does “fractal ordering of...
Prediction of Giant Vortex in Liquid Light!

Article by Dr. Inés Urdaneta, Physicist, Resonance Science Foundation Research Scientist
Photo by Kenji Croman
Just as particles at the very small scale are governed by the strange laws of the quantum world, light can behave weird when placed in the proper conditions. The most intriguing is the case of liquid light that we had addressed in a former article entitled “Liquid light at room temperature”, where light interacts with matter, or more precisely, photons interact with electron-hole pairs – called excitons – in a semiconductor. These excitons impose a dipole moment, which combined with the dipole of the electromagnetic field, couples strongly the excitons and the photons. The result is a polariton, considered a quasiparticle, composed of half-light and half matter which behaves as a Bose Einstein condensate or superfluid even at room temperature. A superfluid behaves like a fluid with zero viscosity. Zero viscosity is equivalent to perpetual...
New Machine Learning Method Raises Questions on the Nature of Reality… Again

By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are increasingly taking the stage, with huge philosophical implications. We have been following this issue in our RSF science blog, first through the article Between the Holographic Approach and Data Science where we addressed the potential of trained artificial neural networks to replace our scientific models, and the possibility of reality being a numerical simulation was discussed. Somehow we had anticipated the work from Vitaly Vanchurin, from the University of Minnesota Duluth, proposing that we live in a neural network and affirming that only through neural networks we could find the theory of everything and grand unification theory. So, our second article entitled Is the universe a Neural network? addressed this later possibility.
Today it was published in Phys.org an article entitled New machine learning method raises question on nature of science which...
More Evidence of Collective Behavior at Cosmological Scale!

Image source here.
By Dr. Inés Urdaneta / Physicist at Resonance Science Foundation
Just a couple of years ago, astronomers and astrophysicists were baffled by the observation of a synchronized behavior in galaxies, which can not be explained by their individual gravitational fields. Such was the case of a study lead by Joon Hyeop Lee, an astronomer at the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute, and published in The Astrophysical Journal in October 2018, reporting hundreds of galaxies rotating in sync with the motions of galaxies that were tens of millions of light years away.
Given the fact that from our known theories, in principle it would be impossible that galaxies separated by megaparsecs (millions of light years) could directly interact with each other, their interaction happens across distances that are too large to be explained by their gravitational force. It is then speculated that some unacknowledged force must be acting.
This discovery came after the...




